What is Git & GitHub? – Create & Merge Branches
🇯🇵 日本語版: 02_Branches.md
This section goes over Git branches and how to work with your first branch.
Overview Overview
- Overview Overview
- git branch command
- Create a new branch
- Add a file to the develop branch
- See the changes on GitHub
- Create & Merge a Pull Request
- Update local repo from GitHub repo
- What is Git Branch?
- Branch and website
- Git Push vs Pull –Teamwork
- Hands-on C Review
- GitHub Workflow
- GitHub Overview-GitHub Website Overview
- GitHub parts
- Quiz time
- Next Section
git branch command
-
First, go back to the
learning_gitrepositorycd Documents/learning_git -
Use
git branchcommand to see all of the branches in your repo & which branch you are currently on.git branch * main
git branch
- git-branch
- Command to display branch list
- The branch with an asterisk (*) is the current branch
- If your default branch name is
master, change it with the following command:git config --global init.defaultBranch main
Create a new branch
First, let’s create a branch named develop and switch to it.
git checkout -b develop
...
Switched to a new branch 'develop'
git checkout -b <branch name>
- This command creates a new branch in the repo & switches to it.
- git-checkout Doc
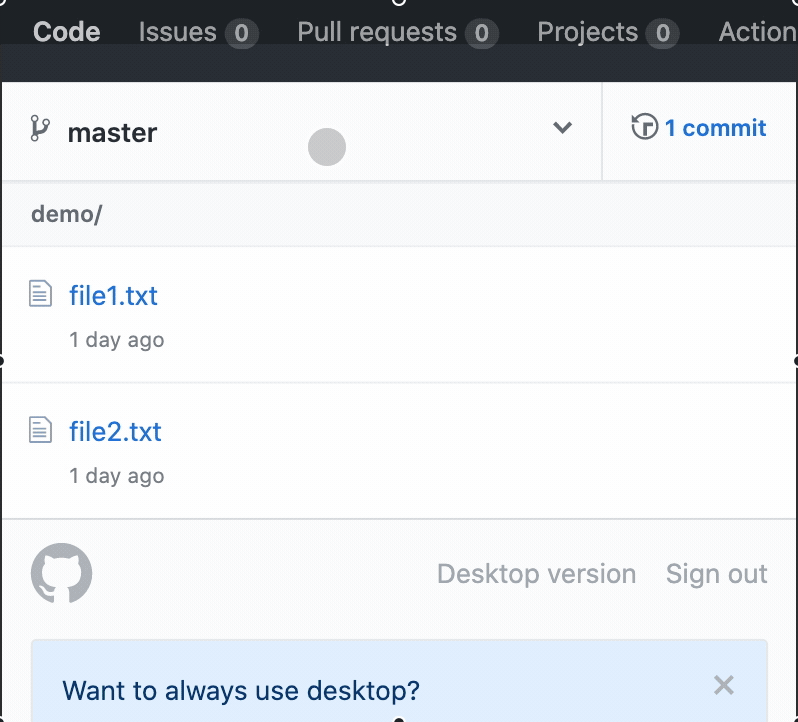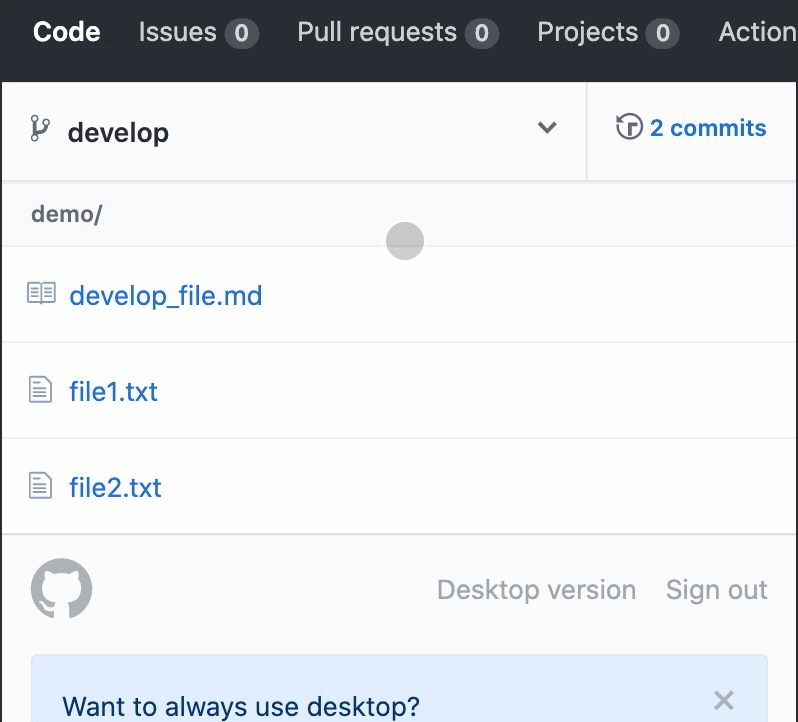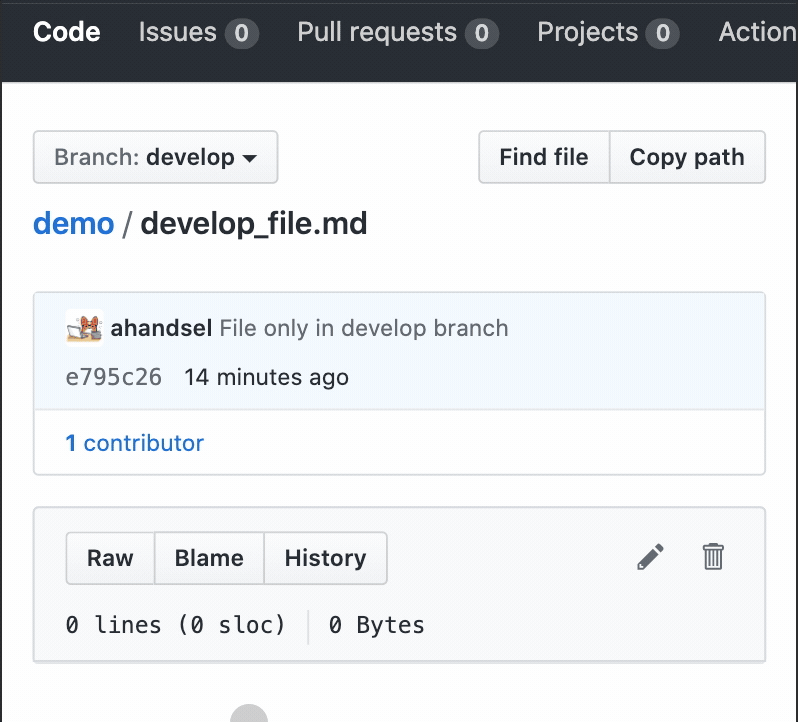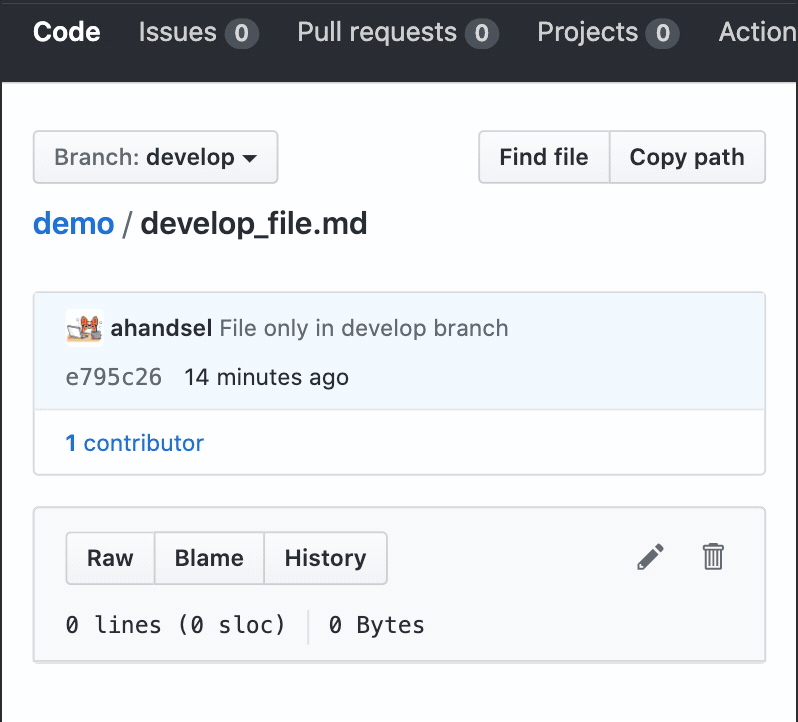
Add a file to the develop branch
-
Create a file on the
developbranchtouch develop_file.md -
Use
git add&git commitcommands to save it in your local repogit add develop_file.md git commit -m "develop only"[develop 4f98baf] develop only 1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) create mode 100644 develop_file.md -
Use
git statuscommand to verify changesgit statusOn branch develop nothing to commit, working tree clean -
Use
git pushcommand to upload changes to GitHubgit push -u origin developEnumerating objects: 4, done. Counting objects: 100% (4/4), done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 277 bytes | 277.00 KiB/s, done. Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 remote: This repository moved. Please use the new location: remote: https://github.com/ahandsel/learning_git_3.git remote: remote: Create a pull request for 'develop' on GitHub by visiting: remote: https://github.com/ahandsel/learning_git_3/pull/new/develop remote: To https://github.com/ahandsel/learning_git_3.git * [new branch] develop -> develop Branch 'develop' set up to track remote branch 'develop' from 'origin'.
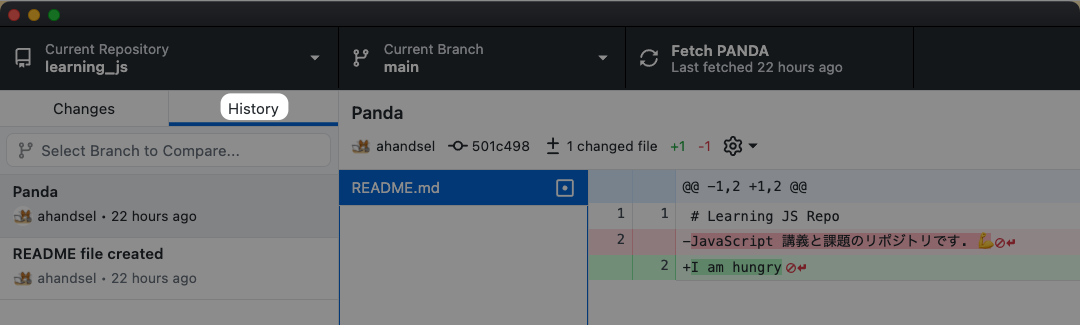
Verify on GitHub Desktop App
Let’s verify the changes by viewing it on the GitHub Desktop App
-
Open the app with the following command:
cd learning_git github . -
App will open to a
Add Local Repositorysetting page, click theAdd Repositorybutton -
Click
HistoryTab to view the changes you have made
See the changes on GitHub
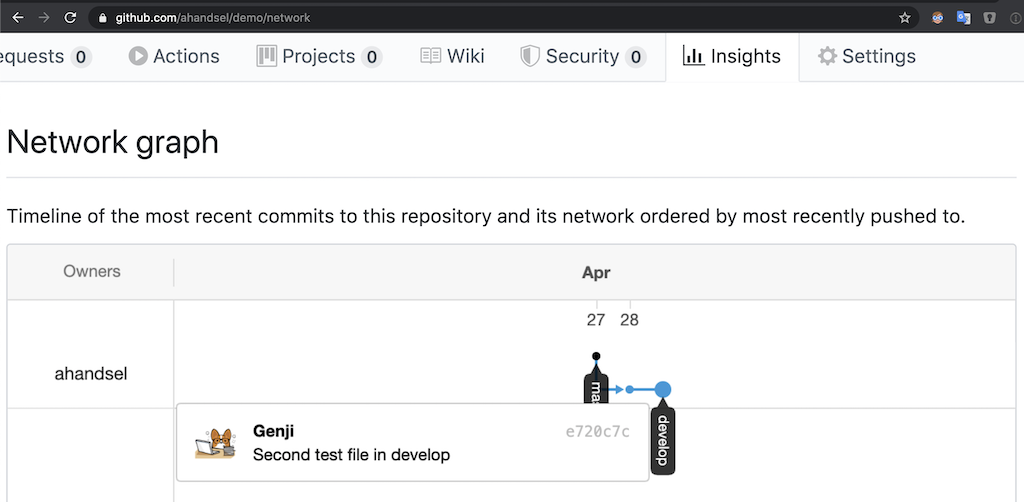
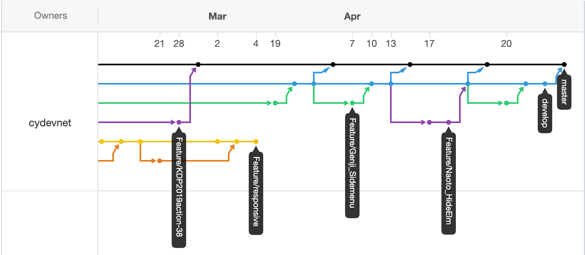
Go to the Network graph setting on your GitHub repo to see the changes you have made
https://github.com/USER/REPO/network- Example:
https://github.com/ahandsel/Git_GitHub_Slides/network
 |
 |
 |
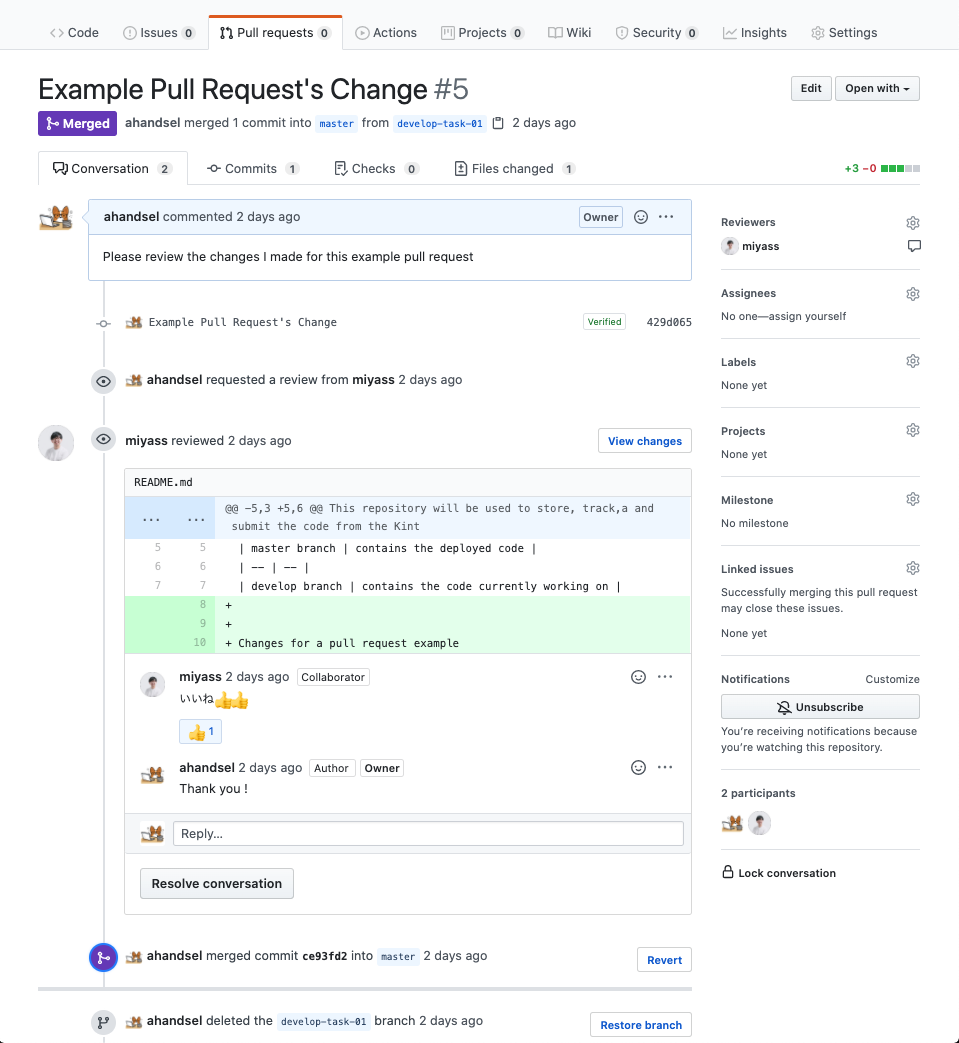
Create & Merge a Pull Request
Pull RequestsSo, you can check other users’ changes etc. before the file is actually changed.
- Used for code reviews, etc.
developCreate in mainGitHub to merge the branch into the branch.Pull request
- Review your changes and
Pull Requestmerge.
mainYou see two new files in your branch!
Update local repo from GitHub repo
main Let’s move to the branch.
git checkout main
Currently, GitHub repositories have more up-to-date files than local repositories.
Switched to branch 'main'
Your branch is behind 'origin/main' by 4 commits & can be fast-forwarded
(use "git pull" to update your local branch)
Use the git pull command to handle this.
Pull the latest version of the repo from GitHub with git pull origin main
git pull origin main
remote: Enumerating objects: 1, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (1/1), done.
remote: Total 1 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (1/1), 631 bytes | 210.00 KiB/s, done.
From https://github.com/ahandsel/kintone_dojo
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
5f9f89b..1438ca5 main -> origin/main
Updating d775d42..1438ca5
Fast-forward
2nd_file.md | 0
develop_file.md | 0
2 files changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 2nd_file.md
create mode 100644 develop_file.md
Now the mainbranch and developthe branch are in the same state,
so developlet’s delete the branch.
git branch -d develop
Deleted branch develop (was c6e6c83).
git branchLet’s check with the command
git branch
* main
What is Git Branch?
What is a branch?
- A moving pointer to the commit.
- It can be managed in multiple timelines and changed without affecting the mainline.
git checkout- Command to switch branches.
git branch -d <branch-name>- Command to delete a branch.
Why use a branch?
- To separate stable version, development version, experimental version, etc.
- Example: This GitHub slide
- Each hands-on and concept section can be a branch.
- You can develop each at the same time.
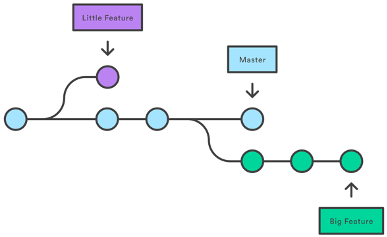
Ref: Git - Branches in a Nutshell
Branch and website
mainIn the branch, there is code that runs the website.
- If
mainchanges are made in the branch, it will affect the user! !!
If two developers want to change their website at the same time, create three branches
main→ Live codefeature_A→ Implemented by developer Afeature_B→ Implemented by developer B
When development is complete, merge the branches!
Git Push vs Pull –Teamwork
git push |
git pull |
|---|---|
| Upload command | Download command |
| “Push” forces changes to the target repository. | “Pull” gets changes from the target repository |
[あなたのコード] ⟾ プッシュ ⟾ [ターゲット] |
[あなたのコード] ⏎ プル ⏎ [ターゲット] |
| A “push request” is a target repository that requests you to push changes. | A “pull request” is to request the target repository to get changes. |
 |
 |
Hands-on C Review
git checkout -b develop |
Command to switch branches |
| Reasons to use a branch | Separate code development, testing, public version, etc. |
Pull RequestsWhengit pull |
A “pull request” is to request the target repository to get changes. |
GitHub Workflow
Understanding the GitHub flow - GitHub Guides
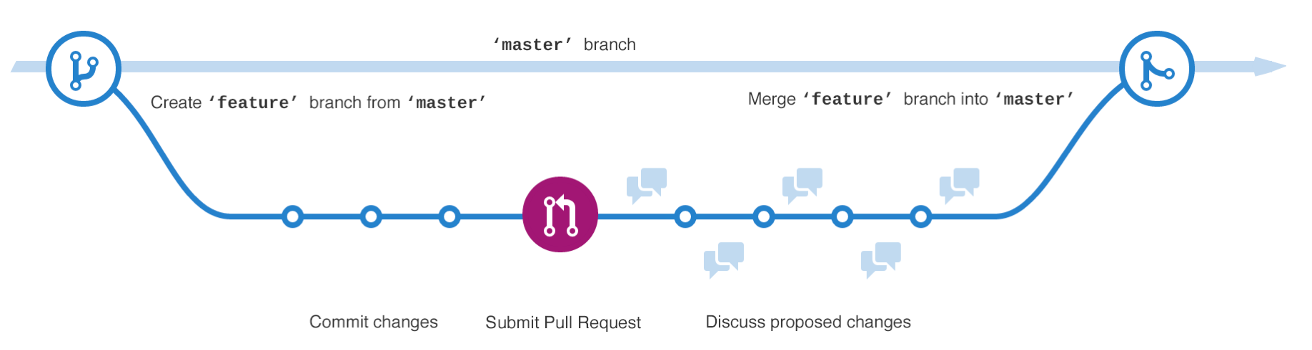
| # | Step | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create a branch | mainfeatureCreate a branch from and start development |
| 2 | Commit changes | After the code implementation is complete, commitcreate. You\ |
commitcan check the change history by creating, and you can roll back and refer to it. |
||
| 3 | Open a Pull Request | When you’re ready to share your implementation with others, create a Pull Request. |
| Four | Discuss & Review Code | Get code reviews from teen members and discuss them. |
| Five | Deploy & Test | Deploy the code to your test environment to make sure it works. |
| 6 | Merge to main | The implementation is now in effect and the Pull Request keeps a record of changes to your code. |
Detailed Overview of the GitHub Workflow
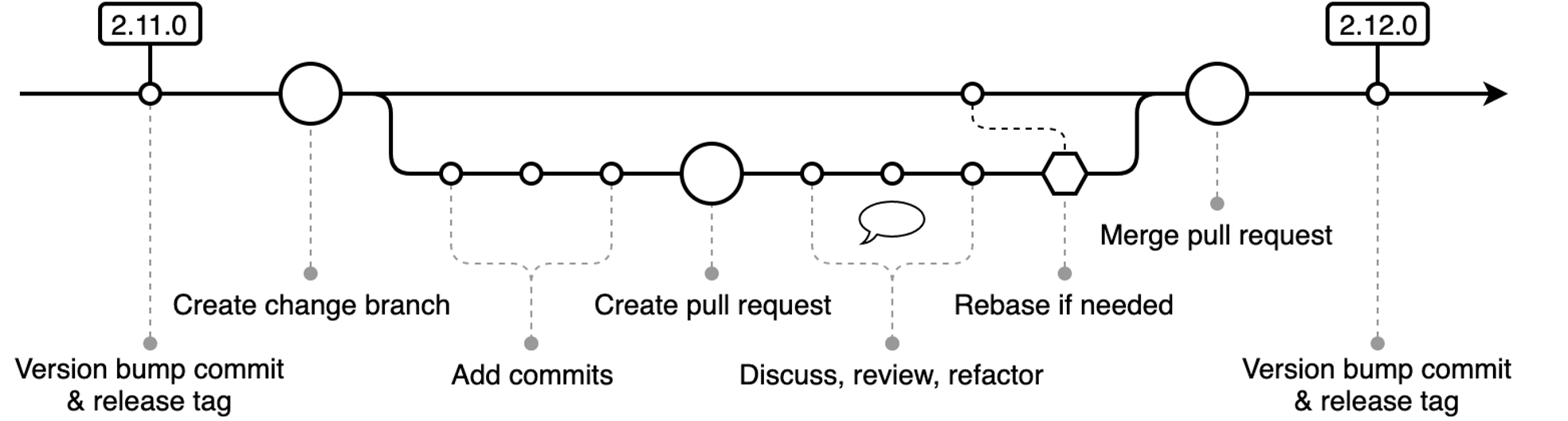
Git Common-Flow 1.0.0-rc.5 –Git Common Flow
GitHub Overview-GitHub Website Overview
GitHub Repository

GitHub Repository –Code
- A container that holds all the files related to your project, such as code and documentation.
- All files stored on GitHub are versioned with git
- Repositories are often abbreviated as “repo”
- It is a file to display the introduction of the project etc. displayed at the bottom of the repository.
GitHub Issues

- Where users discuss the contents of the repository
- You can assign issues to users and add labels to make them easier to read.
GitHub Pull Request

- Used when the user wants to make changes to the repository
- Example: When you want to add a new README.md file
Overview of GitHub
Project boards: Task boards in KANBAN format
Wiki: Allows you to create and save related project documents
Insight: Repository analysis tool
Network Graph: Visualize commits and branches in the timelinePulse: Shows tasks in progress or completed
GitHub parts
| Branch | Code alternative timeline\ |
| example: main, Development, Feature / xxx | |
| Commit | Save file changes to repository |
| Pull Request | Share your proposed changes with others |
| Merge Pull Request | Actually change the branch (main etc.) and update |
Quiz time
- What does the
git checkout -b developcommand do? - Why use a branch?
- What is a
Pull Request?
Next Section
List of Lecture Guides
README_EN.md ⚙️